Firefox 35 was released this week and became the first browser to enable support for the HTTP/2 protocol by default.
The HTTP/2 specification has not been finalised so Firefox actually enabled the Draft 14 version of HTTP/2 but little is expected to change in the final draft. Google is now supporting HTTP/2 draft 14 on its web servers alongside the SPDY protocol giving us a chance to compare the performance of raw HTTPS, SPDY and HTTP/2 on the same web page.
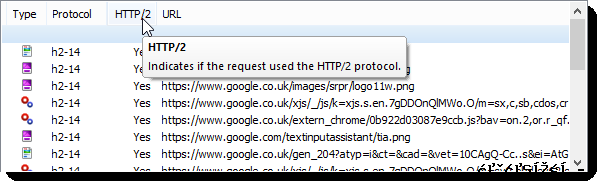
We also updated HttpWatch this week so that it supports HTTP/2 within Firefox. It has new columns to display information about the protocols being used by each request:
The Performance Comparison
The performance test used HttpWatch with Firefox to run a series of simple page load tests against the Google UK home page using the three protocols:
- Raw HTTPS
- SPDY/3.1
- HTTP/2
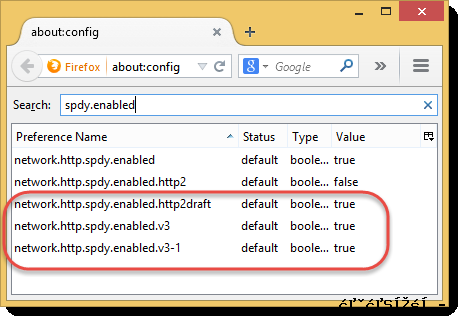
We switched between the protocols by enabling and disabling the following entries in Firefox’s about:config page:
Each test was performed in a fresh instance of Firefox with an empty browser cache. Although this testing was simplistic and only used a simple page it does highlight some important differences between the protocols.
Continue reading »